An Introduction to Essential CNC Machinery Topics
With the myriad options available on the CNC machinery market, selecting and properly caring for the right machine can seem daunting. This post aims to guide readers through the essential considerations. We’ll cover common machine types, comparing CNC machines, maintenance basics, and safety best practices.
Here you can read our article about the difference between :NC vs CNC vs DNC machines and systems.
Key Takeaways
Some highlights include:
- The distinguishing characteristics and applications of CNC lathes and mills
- Weighted criteria for evaluating machine options
- A comparison of vertical and horizontal milling center designs
- Baseline maintenance procedures like lubrication and inspections
- Critical safety protocols around guarding, lockout/tagout and more
Table of Contents
Types of CNC Machinery
CNC machines come in various designs suited for different tasks. Two widely used types are:
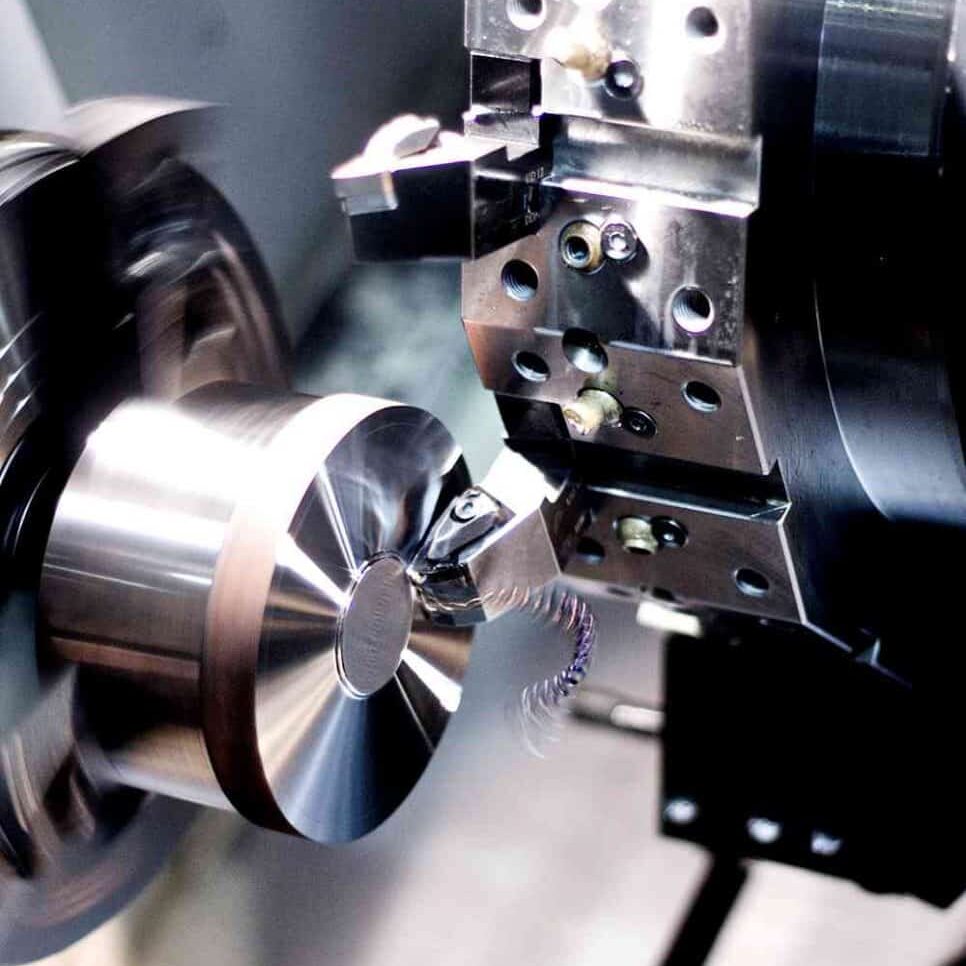
CNC Lathes
Primarily for turning and spinning operations like tapering and grooving components. Parts are rotated as a single cutting tool removes material.
CNC Mills
Designed for planar work like milling, drilling and pocketing. Tools move in the X-Y axes while parts remain stationary.
Beyond lathes and mills, other common CNC tools include routers, grinders, lasers and more. Understanding the basic functions of each machine type is crucial when selecting one for your needs.
Choosing the Right Equipment
Selecting a CNC machine requires weighing factors like your budget, typical workflow, required precision levels and material capacities. Comparing attributes like linear travel distances, spindle speeds and tooling capabilities helps narrow options.
Additional considerations include a machine’s controller, programming software compatibility and integration with accessories. We’ll explore these comparison elements in depth later on. READ Exploring Various CNC Machine Configurations : A Comprehensive Guide
Maintaining Optimal Performance
Proper maintenance plays a key role in maximizing a CNC machine’s productive lifespan. This involves tasks like regular lubrication, cleaning, inspection and part replacements per manufacturer schedules. Neglecting maintenance can potentially lead to costly repairs and downtime.
Through covering these core introduction topics, my goal is to set the stage for readers to make educated choices regarding their CNC machinery needs and long-term stewardship. Let’s begin our deep dive on types, comparisons and optimizing machine uptime.
Types of CNC Machinery
CNC Lathes

Turning Operations
CNC lathes are primarily used for rotational operations that involve rotating the workpiece while a single-point cutting tool removes material. Some common turning functions include:
- Facing – Cutting the end of a cylindrical workpiece square and flat.
- Turning – Reducing the diameter of a cylindrical workpiece to a smaller size.
- Grooving – Cutting axial or circumferential grooves into a workpiece.
- Threading – Cutting external or internal screw threads.
Applications
With their ability to perform intricate spinning processes, CNC lathes are well-suited for applications that involve:
- Automotive parts like pulleys, gears and shafts
- Hardware components like bolts and nuts
- Aerospace cylinders and rotating joints
- Medical devices with cylindrical features
CNC Mills
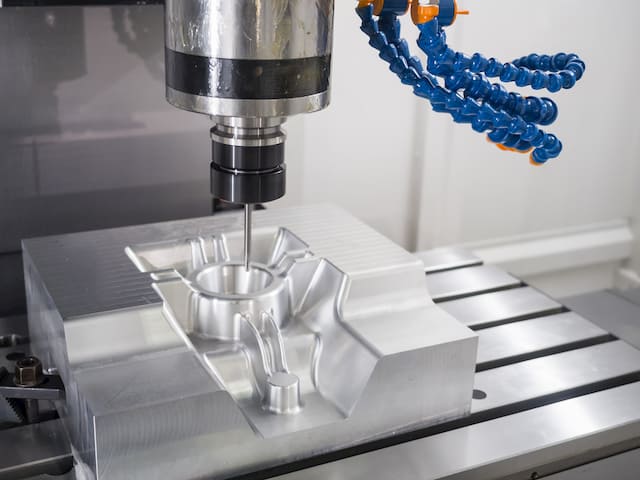

CNC mills excel at planar machining operations involving flat or contoured surfaces. The spindle can be outfitted with tools that cut in the X-Y plane while the part sits securely in the vice.
Read more Understanding the Difference: CNC Routers and CNC Mills
Common Mill Processes
- Drilling – Making holes into or all the way through a workpiece
- End Milling – Flattening or contouring end faces on parts
- Face Milling – Machining flat surfaces parallel to the vice face
- Pocketing – Removing material from profiles or internal cavities
- Profile Cutting – Machining flat or radiused contours along edges
Applications for Mills
The abilities of CNC mills make them a great fit for:
- Dies, molds and other tooling industry applications
- Aerospace brackets, housings and panels
- Medical implants and machined components
- Automotive engine blocks, cylinder heads and housings
CNC Machine Selection and Comparisons
Factors to Consider
When choosing a CNC machine, carefully consider:
- Budget and total cost of ownership
- Available floor space and dimensions
- Expected material types and sizes
- Necessary accuracy and repeatability levels
- Typical workflow needs and processes
No single machine is best in all cases – you must match specs to your specific requirements.
Comparing Mills
Mills further divide into vertical and horizontal designs with pros and cons:
| Vertical Mills | Horizontal Mills |
|---|---|
| Taller machine envelopes | Take less floor space |
| Easier access for large parts | Parts require clearance gaps |
| Greater torque for tougher metals | Higher rapids for lean processes |
Choose based on factors like part geometry, material types and available footprint.
CNC Machine Maintenance
Proper maintenance is key to long-term performance, reliability and accuracy of CNC machinery.
Lubrication
Using the correct lubricants is critical. Refer to manuals for lubrication points and scheduled intervals.
Inspections
Regular inspections evaluate wear on components like ballscrews and linear rails. early detection prevents costly repairs.
Routine Service
Replace filters, belts, coolant and perform enclosure/electrical safety checks per manual schedules. Keep maintenance records.
A strong preventative plan is the backbone of any successful CNC maintenance strategy. Proper Stewardship yields maximum returns over the life of the machine.
I hope this introduction to CNC machinery types, comparisons, and baseline maintenance best practices sets the stage. In future posts, I’ll dive deeper into specific models, advanced processes, and optimization techniques.
CNC Machine Safety and Best Practices
Ensuring safety is paramount with high-speed automated machinery. Adopting proper precautions prevents accidents and protects both operators and expensive equipment.
Machine Guarding
Guarding exposed parts moving at high speeds. Fencing limits access per regulatory standards like OSHA. Interlocks prevent operation if bypassed.
Protective Equipment
Safety glasses, face shields, and other PPE gear guards against flying debris. Hearing protection is vital as well for high-noise environments.
Emergency Stop Functions
Risk of injury warrants clearly labeled E-Stop buttons kept unobstructed. Programmable E-Stops can also halt specific machine zones.
Lockout Tagout Compliance
Strict lockout/tagout procedures should be followed before any servicing. Energy sources are isolated, locked and tagged to prevent unintended startups.
Safe Tool changer Practices
With some machines, automatic toolchanger motions involve risks. Formal training minimizes risks from unintended tool change cycles or movements.
Following standardized safety protocols is a non-negotiable responsibility. Compliance builds a safe working culture and protects both human and financial assets in the long run.
READ Enhancing Your CNC Machine: Must-Have Accessories
Conclusion
In this post, we aimed to provide newcomers with a detailed overview of essential CNC machinery topics. By addressing core areas like common machine types, selection factors, comparative attributes, maintenance best practices, and safety compliance, readers should now have a strong foundational knowledge on these subjects.
Next Steps
To continue enhancing your CNC machinery proficiency:
- Research specific machine brands to identify ideal models
- Consult expert resources for advanced setup, operation and programming
- Consider hands-on training courses for practical expertise
- Join industry groups to learn from experienced professionals
- Monitor new technologies and keep skills up-to-date
Final Thoughts
With a rapidly evolving engineering landscape, maintaining mastery over one’s tools is paramount. I hope this post has equipped you with core insights that serve as a foundation for lifelong learning.
Through diligently selecting the right machines, properly caring for them, and upholding safety as a priority, you’ll optimize operations and unleash your machining potential. Remember to continuously refine and expand your machinery knowledge – the possibilities are endless!
Thank you for learning with us. Please feel encouraged to reach out with any other questions. Now go machine with confidence!


