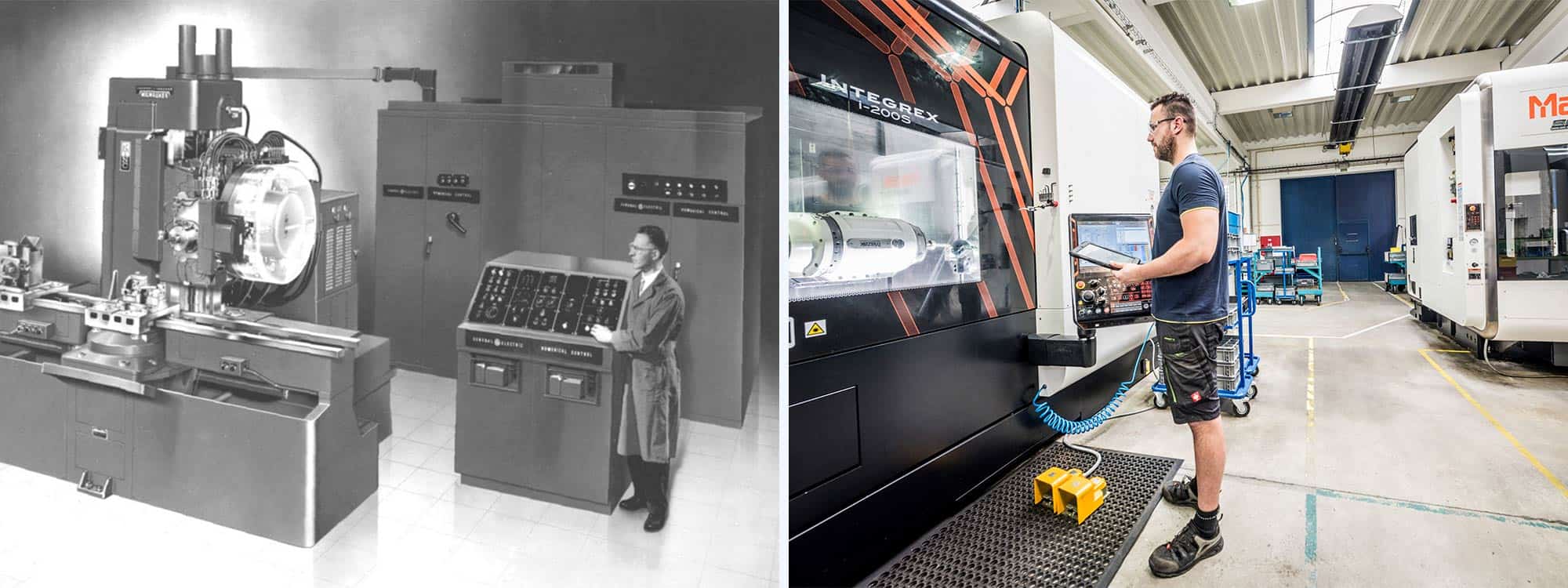
- Introduction
- The Origins of CNC
- Advancements in CNC Technology
- Applications of CNC in Various Industries
- The Future of CNC Technology
- Conclusion
- FAQ
Introduction
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) is a technology that has revolutionized the manufacturing industry. It is a method of controlling machine tools through programmed instructions encoded on a computer. CNC machines have become an integral part of various industries, from automotive and aerospace to furniture and medical equipment manufacturing. In this article, we will delve into the history and advancements of CNC technology, explore The Evolution of CNC , and discuss the future prospects of this game-changing innovation.
The Origins of CNC
The roots of CNC can be traced back to the 19th century when the industrial revolution took place. During this time, the invention of the telegraph paved the way for the development of rudimentary automatic machines. These early machines used punched paper tapes to control their movements, marking the initial steps towards automated equipment.
In the early 1950s, John T. Parsons and Frank L. Stulen developed the first numerical control (NC) system at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). This system utilized punched cards to control the movements of machine tools. However, it was not until the 1970s that CNC technology truly began to gain traction.
Advancements in CNC Technology
The advent of affordable computers and advancements in computing power played a crucial role in the evolution of CNC technology. One significant development was the introduction of the microprocessor in the late 1960s, which made it possible to embed computers directly into the machines.
The transition from analog to digital systems in the 1970s further enhanced the capabilities of CNC machines. Instead of relying on mechanical components, digital systems used electronic signals and binary codes to control machine movements with higher precision and accuracy.
Over the years, CNC machines have continued to evolve, incorporating various technological advancements. The introduction of servo motors and high-speed spindles significantly improved their speed and efficiency. The integration of CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software allowed for seamless model-to-machine translation, reducing errors and increasing productivity.
In recent years, advancements in robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) have further expanded the capabilities of CNC machines. The integration of robots with CNC systems has enabled the automation of complex tasks, reducing human intervention and increasing efficiency.
Learn more about the evolution of machine control systems, including NC, CNC, and DNC
Applications of CNC in Various Industries
The versatility of CNC machines has made them indispensable in a wide range of industries. Here are some examples of how CNC technology is utilized in various sectors:
- Automotive Industry: CNC machines are extensively used in the automotive industry for manufacturing parts and components with high precision. From engine blocks to transmission systems, CNC machines ensure accuracy and consistency, contributing to the overall quality of vehicles.
- Aerospace Industry: CNC technology has revolutionized the aerospace industry by enabling the production of lightweight and complex components. CNC machines are used for machining aircraft parts, such as turbine blades and structural components, with tight tolerances and intricate designs.
- Medical Industry: CNC machines play a vital role in the medical industry by manufacturing custom orthopedic implants, surgical instruments, and prosthetics. The use of CNC technology ensures the precise shaping and machining of these critical medical devices.
- Furniture Industry: CNC machines have transformed the furniture manufacturing process. They are used to cut and shape wood, metal, and plastic materials, allowing for intricate designs and precise joinery. CNC technology has streamlined the production process, reducing the time and cost involved in creating customized furniture pieces.
- Electronics Industry: CNC machines are employed in the electronics industry for manufacturing printed circuit boards (PCBs) and electronic components. They offer high precision and repeatability, facilitating the production of intricate circuitry required in modern electronic devices.
These are just a few examples of the numerous industries that benefit from CNC technology. Its applications extend to sectors such as jewelry, tooling, prototyping, and more.
The Future of CNC Technology

The future of CNC technology looks promising, with several advancements on the horizon. Here are some trends and developments to watch out for:
- Additive Manufacturing: The integration of CNC technology with additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, holds immense potential. This combination allows for the production of complex shapes and structures that were previously impossible to manufacture using traditional machining methods.
- AI and Machine Learning: The incorporation of AI and machine learning algorithms into CNC machines will lead to enhanced automation and optimization. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data, predict machine performance, and optimize cutting parameters, ultimately improving efficiency and productivity.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: Connecting CNC machines to the IoT allows for real-time monitoring of machine performance, remote control, and predictive maintenance. By collecting and analyzing machine data, manufacturers can make data-driven decisions and minimize downtime.
- Collaborative Robotics: Collaborative robots, or cobots, can work alongside humans in shared workspaces. Integrating cobots with CNC machines allows for increased flexibility, improved safety, and the ability to handle more complex tasks.
Conclusion
The evolution of CNC technology has been nothing short of revolutionary. From its humble beginnings as a punched tape control system to the sophisticated machines we see today, CNC has significantly impacted manufacturing across various industries. With advancements in technology and the ever-increasing demand for precision and automation, CNC will continue to play a vital role in shaping the future of manufacturing.
With their ability to automate processes, achieve intricate designs, and deliver consistent results, CNC machines are vital tools that continue to shape the manufacturing industry. The future holds even more opportunities for CNC technology, as advancements in AI, additive manufacturing, and IoT integration promise to further enhance its capabilities. As manufacturing evolves, CNC technology will remain at the forefront, driving innovation and unlocking new possibilities.
FAQ
Q: What does CNC stand for?
A: CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control.
Q: How does CNC technology work?
A: CNC machines are controlled by pre-programmed instructions encoded on a computer. These instructions specify the movements, speeds, and operations to be performed by the machine.
Q: What are the advantages of CNC machines?
A: CNC machines offer increased precision, repeatability, and automation, leading to improved productivity, reduced human error, and faster production times.
Q: Can CNC machines work with different materials?
A: Yes, CNC machines can work with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, and composites.
Q: Are CNC machines expensive?
A: CNC machines range in price depending on their size, capabilities, and complexity. While some machines can be expensive, there are also affordable options available for small businesses and hobbyists.
Q: Can CNC machines be used for prototyping?
A: Yes, CNC machines are widely used for prototyping due to their precision and ability to produce complex shapes and designs.
Q: What is the difference between CNC and traditional machining?
A: Traditional machining requires manual operation and limited precision, while CNC machines operate automatically and offer higher precision and accuracy.
Q: Can CNC machines be used for large-scale production?
A: Yes, CNC machines are used for both small-scale and large-scale production, and their capabilities can be scaled accordingly.
Q: Can CNC machines be adapted for new tasks?
A: Yes, CNC machines can be reprogrammed and adapted to perform different tasks, making them highly versatile and flexible.
Q: Are there any limitations to CNC technology?
A: While CNC machines offer numerous advantages, they do have some limitations, such as initial setup costs, maintenance requirements, and the need for skilled operators.